What is a Gas Spring?
A gas spring, also known as a gas strut or gas lift, is a device that utilizes compressed nitrogen gas within a sealed cylinder to exert a consistent force. This force is harnessed to support, lift, or counterbalance loads in various applications.
Components and Working Principle
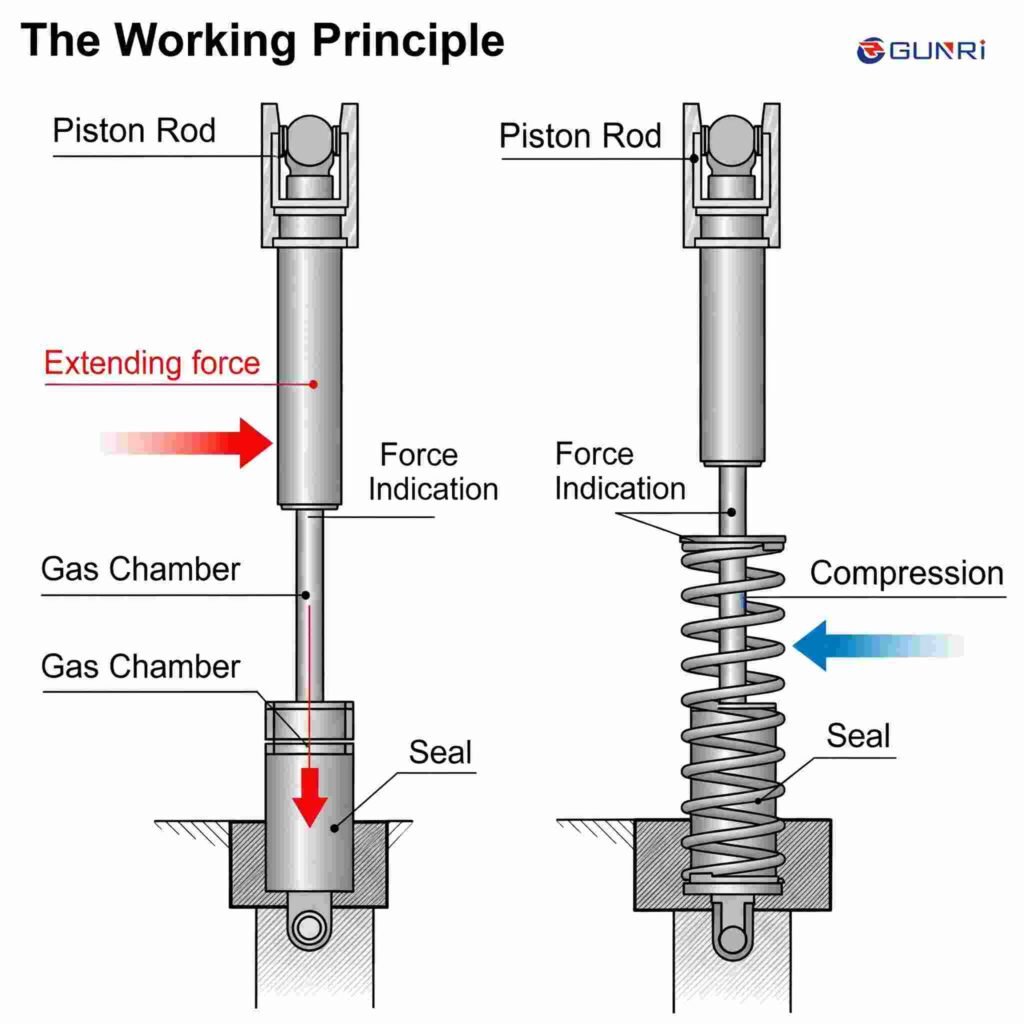
A typical gas spring comprises a piston rod, a cylinder filled with high-pressure nitrogen gas, and a small quantity of lubricating oil. The piston rod moves within the cylinder, and the pressure differential across the piston generates a pushing force.
The gas spring operates by allowing the piston to move within the cylinder, with the gas pressure providing the necessary force. The presence of oil ensures smooth movement, sealing, and damping effects.
Applications
Gas springs are widely used across various industries, including:
- Automotive: Supporting hoods, trunks, and tailgates.
- Industrial Machinery: Assisting in the opening and closing of machine covers.
- Furniture: Facilitating adjustable chairs and recliners.
- Medical Equipment: Enabling smooth operation of adjustable beds and chairs.
- Fitness Equipment: Providing controlled resistance in exercise machines.
- Mold Equipment: Assisting in the ejection of molded parts.
Advantages of Gas Springs
- Initial Force Availability: Gas springs provide significant force from the start of compression, unlike traditional metal springs.
- Consistent Force Output: They maintain relatively constant force throughout the stroke.
- Compact and Lightweight: Despite their small size, they can exert substantial force.
- Versatile Functionality: Available in various types, including damped, adjustable, compression, and tension models.
Selecting the Right Gas Spring
When choosing a gas spring, consider the following factors:
- Force Calculation: Determine the required force (F) based on the weight of the object and the number of springs used. It’s advisable to add a 10% safety margin to the calculated force.
- Maximum Length: Ensure the fully extended length of the gas spring is slightly longer than the maximum distance between mounting points during operation.
- Stroke Length: The stroke should accommodate the range of motion required, with an additional 5–10mm to prevent overextension.
- Mounting Configuration: Choose appropriate end fittings and mounting orientations to suit the application.
Installation Guidelines
- Orientation: Install the gas spring with the piston rod facing downward to ensure optimal lubrication and damping.
- Alignment: Avoid side loads or misalignment to prevent bending or damage.
- Surface Protection: Keep the piston rod clean and free from scratches, paint, or chemicals to maintain sealing integrity.
- Temperature Range: Operate within the specified temperature limits, typically -30°C to +80°C.
- Mounting Points: Ensure pivot points are free-moving and not obstructed.
- Safety Precautions: Do not disassemble, puncture, or expose the gas spring to fire or high heat, as it contains high-pressure gas.
Common Applications
- Horizontal Opening: Used in applications where panels open horizontally.
- Upward Side Opening: Ideal for side panels that open upwards.
- Downward Side Opening: Suitable for panels that open downwards from the side.





